MEDIZIN
AWARDS
Forschergeist gefragt: 14. Novartis Oppenheim-Förderpreis für MS-Forschung ausgelobt
FernstudiumCheck Award: Deutschlands beliebteste Fernhochschule bleibt die SRH Fernhochschule
Vergabe der Wissenschaftspreise der Deutschen Hochdruckliga und der Deutschen Hypertoniestiftung
Den Patientenwillen auf der Intensivstation im Blick: Dr. Anna-Henrikje Seidlein…
Wissenschaft mit Auszeichnung: Herausragende Nachwuchsforscher auf der Jahrestagung der Deutschen…
VERANSTALTUNGEN
Wichtigster Kongress für Lungen- und Beatmungsmedizin ist erfolgreich gestartet
Virtuelle DGHO-Frühjahrstagungsreihe am 22.03. / 29.03. / 26.04.2023: Herausforderungen in…
Pneumologie-Kongress vom 29. März bis 1. April im Congress Center…
Die Hot Topics der Hirnforschung auf dem DGKN-Kongress für Klinische…
Deutscher Schmerz- und Palliativtag 2023 startet am 14.3.
DOC-CHECK LOGIN
Bone manifestations in Gaucher disease
Gregory M. Pastores, MD
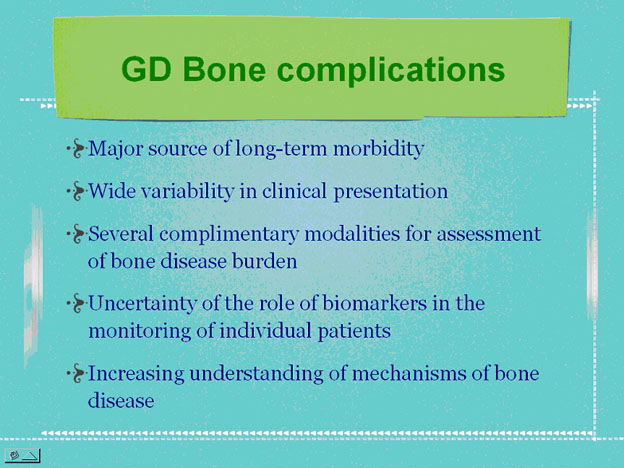
Munich (12. September 2008) – Bone involvement associated with glucocerebrosidase deficiency represents a major source of morbidity for patients with Gaucher disease (GD); primarily those with the type I and III clinical variants. Bone findings can range from mild asymptomatic osteopenia to osteonecrosis with subchondral joint collapse and secondary arthritis. As a consequence, in the most severely affected patients there are risks of secondary neurologic complications from spinal cord compression or radiculopathy (nerve root entrapment), and complaints of chronic bone pain/discomfort and limitations in joint range of motion; and in some cases requiring surgical intervention. There are indications of a multifactorial basis for the observed bone complications; initiated by the progressive accumulation of incompletely metabolized lipids within macrophages, recruitment and activation of osteoclasts and other factors. Various radiologic and imaging modalities are available to assist with defining the pattern and severity of bone disease, complemented by testing of markers of bone turnover in blood and urine.
However, there are significant challenges in assignment of risks of bone-related complication, and in the staging of bone disease and measuring disease progression. The complexity of dealing with bone disease in GD is partly due to the fact that: 1) bone findings in an individual patient can vary across several anatomic sites, and may be discordant with systemic extra-skeletal disease burden’, 2) markers of bone turnover have not shown consistent abnormalities or proven to be of use in management; and 3) measurable bone changes take time to demonstrate. Treatment with enzyme therapy appears to have modified the natural course of bone disease; particularly among those who have initiated treatment prior to skeletal maturation.
A pooled analysis of data on bone-related outcomes collected prospectively over 2 years from patients in three multinational, open-label, clinical trials with miglustat was recently analyzed. The effect of the drug of bone manifestations were reported based on 72 patients with GD1, of whom 57 % had received previous ERT, and 28 % had undergone splenectomy. The overall median treatment duration with miglustat was 568 days. Miglustat treatment has resulted in improved ‘bone marrow burden’ score, reduction of bone pain and increased bone mineral density. Of the 24 patients with no bone pain at baseline, 92 % remained pain free throughout Miglustat therapy. Further, no cases of bone crisis or avascular necrosis occurred during the 2-year treatment period. Significant increases in BMD Z-scores from baseline were measured at 6 months, 12 months and 24 months across the whole patient cohort.
Further studies may provide additional insights into the mechanisms that underlie the GD bone involvement and point us towards potential avenues of optimal management; particularly in the longterm maintenance phase of treatment.

Slide 1

Slide 2

Slide 3
Author
Gregory M. Pastores, MD
Associate Professor
Neurology and Pediatrics
NYU School of Medicine
New York, NY, USA
Quelle: Satelliten-Symposium der Firma Actelion zum Thema „Lyosomale Speichererkrankungen: selten gesehen – oft übersehen“ am 12.09.2008 in München, anlässlich der 104. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin (CGC Cramer-Gesundheits-Consulting) (tB).